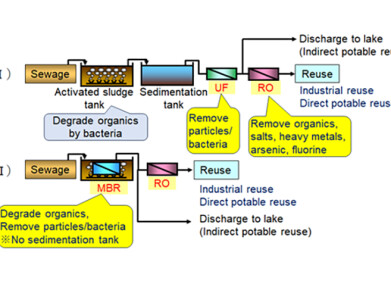
Water/Wastewater
Cost-cutting wastewater project could slash greenhouse gas emissions
Mar 27 2024
The University of South Wales (USW) is pioneering a groundbreaking project aimed at significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with wastewater treatment. Partnering with Dŵr Cymru Welsh Water (DCWW), the project, dubbed 'OXYHYWATER,' holds promise for substantial cuts in environmental impact.
Developed by the USW-based Sustainable Environment Research Centre (SERC), OXYHYWATER introduces a novel wastewater treatment approach utilising pure oxygen instead of atmospheric air. Early findings indicate a multitude of environmental benefits stemming from this innovative method.
Professor Alan Guwy, Head of SERC and project lead, highlighted the cost-effectiveness of using pure oxygen compared to atmospheric air. Moreover, this approach minimises secondary biomass generation, reducing both costs and energy demands for waste treatment. Importantly, OXYHYWATER's enclosed design and pure oxygen usage also promise significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, particularly nitrous oxide, known for its potent global warming potential.
The oxygen utilised in OXYHYWATER is a byproduct of hydrogen production via electrolysis, aligning with environmentally friendly practices. Dr. Jaime Massanet-Nicolau, Associate Professor of Bio-Based Chemical Production and Co-Investigator, emphasised the synergy between OXYHYWATER and electrolysis, where discarded oxygen finds purpose in wastewater treatment.
Furthermore, OXYHYWATER offers additional environmental advantages through its advanced filtration system. Dr. Massanet-Nicolau explained how the system's unique membranes retain microbes, allowing for more efficient water treatment and reduced energy consumption.
The journey of OXYHYWATER from lab-scale development to pilot implementation underscores a collaborative effort between SERC, DCWW, and various funding bodies. Supported by initiatives like the ERDF Reducing Industrial Carbon Emissions (RICE) project and the UKIR-funded IDRIC research program, the pilot-scale OXYHYWATER system now operates at a wastewater treatment plant in South Wales.
In essence, OXYHYWATER represents a significant step towards sustainable wastewater treatment, offering not only cost-effective solutions but also substantial reductions in greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption, all while leveraging innovative technologies and collaborative partnerships.
Events
May 05 2024 Seville, Spain
May 13 2024 Munich, Germany
May 23 2024 Beijing, China
May 23 2024 Beijing, China
Jun 10 2024 Algiers, Algeria