Liquid Handling
Precise solutions for low flow liquid measurement
Mar 16 2024
Low-flow measurement is increasingly prevalent across various industries. Yet, as flow rates decrease, the task of controlling and measuring them becomes progressively more challenging. This poses a significant obstacle for users and flow sensor manufacturers alike in their search for cost-effective and reliable flow measuring technologies.
While there isn't a standardized definition for ‘low flow’ concerning fluidics handling, these applications face distinct challenges compared to larger flows. The minimal volume of liquid involved makes low-flow systems highly sensitive, amplifying concerns about flow stability and performance. Even minor disruptions in process or environmental conditions can significantly affect flow stability in low-flow scenarios.
In the markets where Titan Enterprises operates, low flow rates are considered to be those below 50 ml/min, with many customers seeking flow rates ranging from 2 to 20 ml/min.
Neil Hannay, Senior R&D Engineer at Titan Enterprises, noted: "We are observing a significant rise in the demand for low flow measurement technologies, fuelled by various industries shifting towards transporting highly concentrated liquids that are later diluted at the point of use. This transition results in substantial savings on transportation and storage expenses, while also yielding positive environmental benefits."
From cleaning fluid additives to beer or soda syrups and flavourings, chemical additives for oil and fuel, paint pigments, or drug administration, the use of low-flow flowmeters is essential. They ensure precise dosing of these concentrated fluids at the end of the process, facilitating accurate dispensing for the correct dilution.
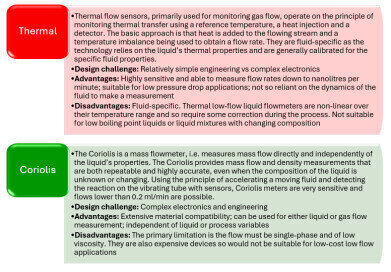
As mentioned, measuring low flow presents a challenging application to address. The energy available in low liquid flow is often inadequate to drive most mechanical flowmeters to provide linear results. Electronic flow meters, on the other hand, may face limitations such as sensitivity, zero drift, and slow response times. This analysis covers five types of flow meter - Ultrasonic, Turbine, Oval Gear, Thermal, and Coriolis - and assesses their suitability for low flow measurement.
Selecting the most appropriate high-precision flow sensor for your application is crucial, as flowmeters can often be the most constraining element of a low flow fluidic system.
Neil stated: "We recognise a robust market demand for low flow meters, and we are presently collaborating with two international OEMs to devise a solution for measuring ultra-low flows leveraging our oval gear technology and miniaturised gears."
More information online
Digital Edition
ILM 49.5 July
July 2024
Chromatography Articles - Understanding PFAS: Analysis and Implications Mass Spectrometry & Spectroscopy Articles - MS detection of Alzheimer’s blood-based biomarkers LIMS - Essent...
View all digital editions
Events
Jul 28 2024 San Diego, CA USA
Jul 30 2024 Jakarta, Indonesia
Jul 31 2024 Chengdu, China
ACS National Meeting - Fall 2024
Aug 18 2024 Denver, CO, USA
Aug 25 2024 Copenhagen, Denmark





24_06.jpg)













