Microscopy & Microtechniques
Optical Rheology Stage used to Investigate LCP Polymer Blends
Jun 13 2013
Linkam Scientific Instruments report on the use of their popular CSS450 stage for polymer research at the New University of Lisbon, Portugal.
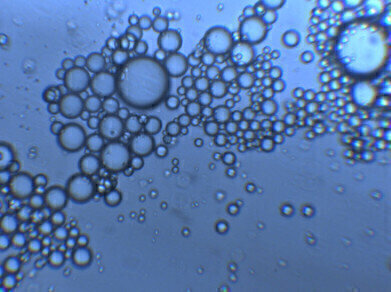
Associated with the Department of Materials Science, University of Lisbon, CENIMAT (a national scientific research centre in Portugal) is devoted to developing radical new approaches in the areas of structural, electronic and optoelectronic, polymeric and mesomorphic, dielectric and electroactive materials. Professor Maria Teresa Cidade and her colleagues are looking at the fibrillation mechanisms within two blends of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) with a liquid crystalline polymer, Rodrun LC3000 (10 and 25 wt % LCP content). The scientists' initial studies of the blends using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) showed that the 10wt% blend had no fibrils, yet the 25wt% blend did have some evidence of fibrillation. To better understand the mechanical behaviour of the polymer blends, the scientists used the Linkam CSS450 stage to study the rheo-optical properties.
Professor Cidade commented "the Linkam CSS 450 Shearing System allows us to follow the morphology/texture of different kind of fluids such as liquid crystals, emulsions and composites." Using the CSS450, the structural dynamics of complex fluids can be directly observed using a standard optical microscope while under precisely controlled temperature and shear modes. The microstructure evolution of complex fluids can be studied in great detail for many physical processes. This allows the correlation of the micro structural dynamics with rheological data to gain insight into the rheology of complex fluids. The images captured can also be used to validate numerical results from computer simulations and experimental data from indirect measurements such as using scattering techniques.
Samples were observed for droplet size and deformation under varying shear rates It was shown that the blend with the lower LCP content had minimal relaxation times which did not increase exponentially for higher shear rates. The blend with the higher LCP content showed increasing relaxation times in parallel with the increase of shear rate. Professor Cidade explained, "We found that the droplet shape relaxation time (the time the deformed droplet takes to regain its spherical form after cessation of flow) allowed for the explanation of the morphological observations."
Digital Edition
ILM 49.5 July
July 2024
Chromatography Articles - Understanding PFAS: Analysis and Implications Mass Spectrometry & Spectroscopy Articles - MS detection of Alzheimer’s blood-based biomarkers LIMS - Essent...
View all digital editions
Events
Jul 28 2024 San Diego, CA USA
Jul 30 2024 Jakarta, Indonesia
Jul 31 2024 Chengdu, China
ACS National Meeting - Fall 2024
Aug 18 2024 Denver, CO, USA
Aug 25 2024 Copenhagen, Denmark


24_06.jpg)













