Laboratory Products
150 Years On: How the Periodic Table Was Created
Oct 02 2019
Today, the Periodic table graces the walls of science classrooms and university laboratories around the world. What many people don't know is that the tabular display of chemical elements was pioneered more than 150 years ago by Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian chemist who was once of the first to perceive the relationships between the elements.
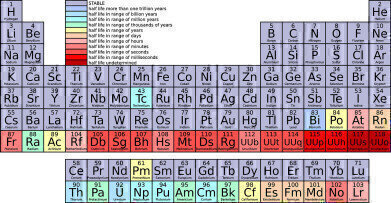
The Periodic table currently lists 118 confirmed elements, with each square containing a unique set of symbols and numbers. These numeric and symbolic signatures reveal patterns and connections in the properties of each element and serve as a guideline for chemical research.
“The Periodic table,” writes celebrated English and University of Oxford fellow Peter Atkins, “is arguably the most important concept in chemistry.”
From hand drawn sketch to scientific lore
While today the Periodic table is considered something of a scientific bible, the original chart drawn up by Mendeleev was little more than a hand drawn sketch. He executed his vision to arrange the elements in order of their atomic weights and as a result, was able to pinpoint familial relationships. These similar properties appeared at regular intervals, or periods, as Mendeleev referred to them.
“Elements arranged according to the size of their atomic weights show clear periodic properties,” said Mendeleev, who formulated the Periodic Law in 1869. “All the comparisons which I have made … lead me to conclude that the size of the atomic weight determines the nature of the elements.”
Predicting new elements
This discovery allowed him to not only refine the properties of known elements, but also predict the properties of eight elements that were not yet discovered at the time. When translated from Russian, the title of the original Periodic table sketched by Mendeleev reads, “Draft of system of elements: based on their atomic masses and chemical characteristics.”
“Before the promulgation of this law the chemical elements were mere fragmentary, incidental facts in Nature,” said Mendeleev. “The law of periodicity first enabled us to perceive undiscovered elements at a distance which formerly was inaccessible to chemical vision.”
The early pioneers of the Periodic table
While Mendeleev received most of the credit for developing the Periodic table, recognition should also be given to German chemist Johann Wolfgang Dobereiner, who explored the concept of grouped elements in the early 1800s. English schoolteacher John Dalton also contributed to early research, explaining the mechanics behind chemical reactions in his 'New System of Chemical Philosophy' published in 1842.
Over the years, the Periodic table has evolved and undergone updates and additions. Some of the newest additions include Nihonium, Moscovium, Tennessine and Oganesson, which were approved by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry and added to the table in 2016.
From Mendeleev to Hawking, scientists are continually pioneering new breakthroughs. For an introduction to the latest updates made to technologies manufactured by Austrian company Anton Paar, don't miss 'Digital Density Measurement Redefined.'
Digital Edition
Lab Asia 31.2 April 2024
April 2024
In This Edition Chromatography Articles - Approaches to troubleshooting an SPE method for the analysis of oligonucleotides (pt i) - High-precision liquid flow processes demand full fluidic c...
View all digital editions
Events
Apr 25 2024 Istanbul, Turkey
Apr 28 2024 Montreal, Quebec, Canada
May 05 2024 Seville, Spain
InformEx Zone at CPhl North America
May 07 2024 Pennsylvania, PA, USA
May 14 2024 Oklahoma City, OK, USA