Microscopy & Microtechniques
Qdots use viruses to fool cancer cells
Feb 17 2012
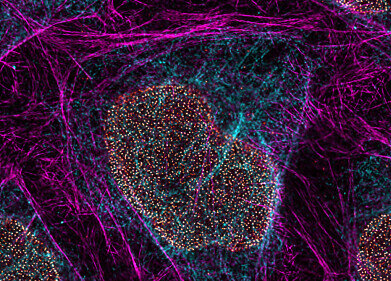
New nanotechnology has exploited virus mechanisms that fool cancer cells in order to transport Quantum Dots (Qdots) into brain cancer cells and bind them to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR).
Previously, there have been difficulties getting the Qdots into cells without them clumping, or being packaged in to endosomes, and excreted from the cells as waste. However, researchers from the City College of New York overcame this problem by coating the Qdots in lipid and protein coats based on Sendai virus.
Prof Maribel Vazquez explained: "While cells have complex defence mechanisms to protect themselves against attack, viruses have evolved ways to fool the cell into letting them in."
"Once inside the cell, the Qdot-antibody complexes were able to bind to the receptor and the amount of bound complex could be monitored by measuring Qdot fluorescence."
Qdots can be linked to biological molecules, such as antibodies, and can then make it easy to find which cells contain the protein the antibody recognizes, and where in the cell this protein is located.
Posted by Ben Evans
Digital Edition
Lab Asia 31.2 April 2024
April 2024
In This Edition Chromatography Articles - Approaches to troubleshooting an SPE method for the analysis of oligonucleotides (pt i) - High-precision liquid flow processes demand full fluidic c...
View all digital editions
Events
May 21 2024 Lagos, Nigeria
May 22 2024 Basel, Switzerland
Scientific Laboratory Show & Conference 2024
May 22 2024 Nottingham, UK
May 23 2024 Beijing, China
May 28 2024 Tel Aviv, Israel








.jpg)