Microscopy & Microtechniques
Report on the Application of Micromanipulators and SEMGlu to Study Materials from the Nuclear Power Plant Accident at Fukushima
Jan 24 2017
PhD student, Peter Martin, is a member of the School of Physics at the University of Bristol. His research focuses on the March 2011 incident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) in Japan and its effects at both the metre and micron scales.
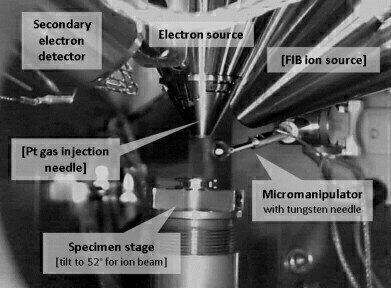
Only a few studies were being performed on material collected from air sampling filters at a few locations close as well as further away from the plant. Previous work within the Interface Analysis Centre at the University of Bristol has extensively used Kleindiek MM3A-EM Micromanipulators from EM Resolutions for a range of applications. By using micromanipulators in their work, they are able to remove only the particles of interest (after identifying material under the SEM). In this way, they are able to obtain the most accurate isotopic analysis results in addition to having the samples mounted for an array of further analytical techniques. Micromanipulators such as the Kleindiek MM3A-EM installed within an SEM represent the only method to remove the sub-nanometer fallout particles encountered.
When asked about his choice of manipulator, Martin said: “Kleindiek MM3A Micromanipulators are used in our work for other applications as well as the ‘particle picking’ described above. The main advantage of Kleindiek system is their flexibility in operation. Unlike other systems which provide a method of manipulating a needle, the Kleindiek platform can be used for a whole range of applications and is not limited as a niche instrument.”
Continuing, Martin talked about the experimental methods used. “Using electrostatic attraction between objects and manipulation needles is the common way with which to ‘pick-up’ material. However, in order to ensure that these highly active particles remain attached and do not ‘fall off’ representing a large radiological hazard, the use of Kleindiek SEMGlu has been very important. The very high strength of this vacuum compatible adhesive, which is polymerised under the electron beam, means that the particles are well-adhered for transport and remain on the needle tip during the range of analytical techniques that are carried out on them whilst still attached to the manipulation needle (tungsten or glass). Like the Kleindiek systems in general, other uses for outside of ‘particle picking’ have been explored within the group.”
Digital Edition
Lab Asia 31.2 April 2024
April 2024
In This Edition Chromatography Articles - Approaches to troubleshooting an SPE method for the analysis of oligonucleotides (pt i) - High-precision liquid flow processes demand full fluidic c...
View all digital editions
Events
Apr 25 2024 Istanbul, Turkey
Apr 28 2024 Montreal, Quebec, Canada
May 05 2024 Seville, Spain
InformEx Zone at CPhl North America
May 07 2024 Pennsylvania, PA, USA
May 14 2024 Oklahoma City, OK, USA