Microscopy & Microtechniques
Tensile Stage Used to Assist with the Development of New Materials that Address Eye Healthcare in the Ageing Population
Oct 27 2015
Professor Rachel Williams is Professor of Ophthalmic Engineering at the Institute of Ageing and Chronic Disease at the University of Liverpool.
The major aim of her research group is to develop advanced materials to address the growing burden of eye healthcare in the ageing population. Underpinning these developments is the design and production of advanced materials with key features that drive the biological response required to overcome the destructive nature of the disease. Two particular areas where the Linkam system is applied are in: 1) the design and development of novel materials for contact lenses and 2) the design of advanced gels to replace damaged corneas.
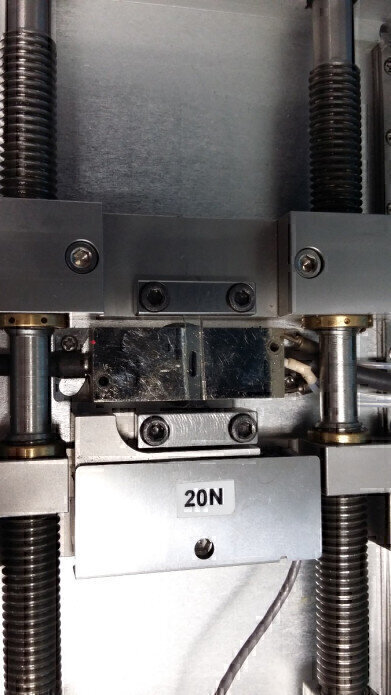
The motivation for incorporating such a stage in the workflow of this research comes from the ability to characterise the mechanical behaviour of gels. A high water content transparent gel can be produced from poly-ε-lysine and cross-linked with multifunctional carboxylic acids. Describing their results, Professor Williams said: “With the Linkam TST stage, we have shown that mechanical properties can be controlled by the nature and density of the cross-links to produce a gel with properties similar to existing contact lenses.” Development of these gels as contact lens materials will underpin the development of a new generation of infection resistant contact lenses.
The second part of the programme is to design and develop the platform of gel-like materials for the production of a tissue equivalent for complete corneal replacement. Conventionally, corneal diseases have been treated with full thickness corneal transplantation but there is a chronic shortage of cornea available for transplantation. There would be significant advantages from the development of a synthetic tissue equivalent. The surfaces of the gels need to promote the attachment and growth of corneal epithelium and endothelium each of which grow on a defined basement membranes. Once again, the group is using the Linkam system to optimise the properties of these gels.
Talking about the advantages of using the Linkam TST stage, Professor Williams continued: “While temperature control is not important for our research, the benefit of using the Linkam stage is that our samples are very small and difficult to handle. It would not be possible to test them in a vertical system whereas the horizontal stage of the Linkam system works well for us. The small scale of the whole stage also means it can be put inside a cell culture incubator if necessary.”
Digital Edition
Lab Asia 31.2 April 2024
April 2024
In This Edition Chromatography Articles - Approaches to troubleshooting an SPE method for the analysis of oligonucleotides (pt i) - High-precision liquid flow processes demand full fluidic c...
View all digital editions
Events
Apr 28 2024 Montreal, Quebec, Canada
May 05 2024 Seville, Spain
InformEx Zone at CPhl North America
May 07 2024 Pennsylvania, PA, USA
May 14 2024 Oklahoma City, OK, USA
May 15 2024 Birmingham, UK